Digital transformation is a key priority of the government and its work with the Inter-American Development Bank. Bold steps towards advancing this agenda are underway, including the establishment of a dedicated Ministry of Digital Transformation in 2021. In this five-part series we will explore opportunities for digital transformation in T&T’s grocery eco-system and learn how some retailers are already redefining their businesses to compete in the post-pandemic era.
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, digital grocery systems were unexplored and unavailable options for most shoppers in Trinidad & Tobago. Consumers felt reasonably well served by traditional supermarkets and the in-store shopping experience of browsing through aisles, comparing goods and “feeling the cabbage” to select the best quality produce. Then came COVID-19 with its lockdowns and social distancing which forced the consumer to consider different ways of shopping for their groceries. Today, as the region recovers, there is a significant change in the way businesses, including groceries, operate with a massive shift to online activity and the use of digital technologies.
Timing couldn’t be more ideal as this shift in consumer behavior coincides with both the implementation of the IDB’s Vision 2025 and the IDB Country Strategy with Trinidad and Tobago (2021-2025) to support digital transformation and accelerate recovery in the region after the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Both plans aim at implementing the IDB’s institutional strategy with two objectives – short term, that involve digital transformation support and medium-term objectives including the promotion of sustainable and inclusive growth through the reactivation of the productive sector. Both objectives can be satisfied by collaborating with stakeholders in the local grocery environment, as the desire to digitally transform is high amongst vendors large and small who recognize that transformation is the key to long-term business success.
Digital grocery transformation
Advancements in digital grocery transformation represent a paradigm shift in the grocery model from the traditional brick and mortar of the past to today’s digital ecosystem. This ecosystem is built on the processes and enablers needed for a smooth, efficient flow of transactions and customer-purchase experiences. It involves the digital consumer placing an order through an automated picking and supply chain management system and then making a purchase to allow for a satisfied customer. The graph 1 demonstrates the Processes & Enablers of the Digital Grocery Ecosystem.
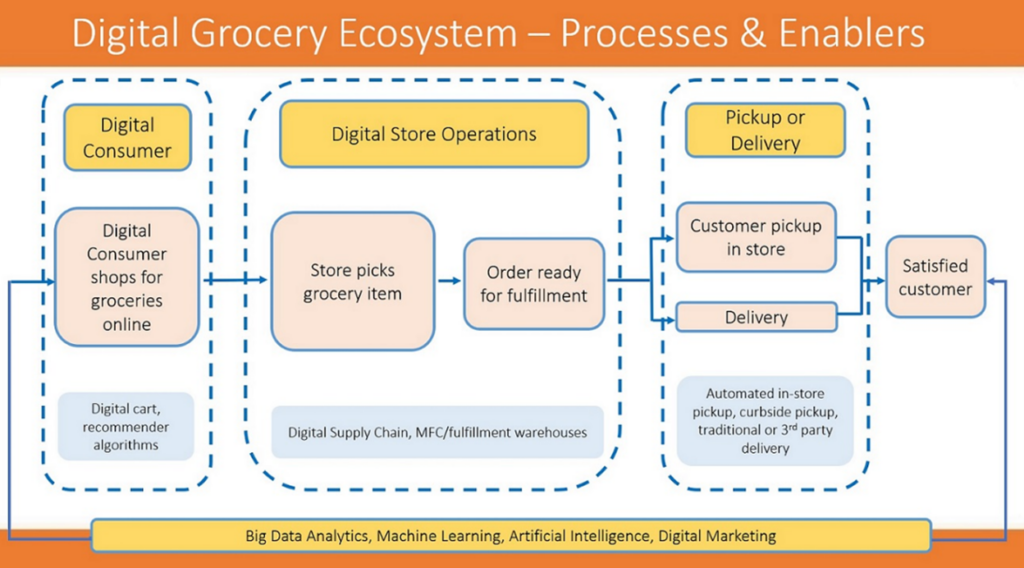
A key component of customer satisfaction is a seamless, user-friendly experience that provides accurate online ordering across all categories. In today’s digital retail landscape, retailers must place greater emphasis on building an attractive “digital shelf” to facilitate a high-quality e-commerce experience and leverage big data technology to better understand customer behavior and shifting trends in their preferences and needs.
Digital store operations encompass technology and infrastructure necessary for the efficient processing of digital consumers’ online grocery orders. The digitally connected supply chain can identify the appropriate inventory necessary to support customer demand, define the cost to serve, and make real-time decisions that will focus on the outcomes. Advanced GPS technology has spurred innovation in automated grocery pickup, where curbside pickup and delivery service options make that final purchase easier than ever to get in hand for the consumer.
Even here in Trinidad and Tobago, we have seen an evolution in the operation of the grocery sector, with some businesses adding digital channels as part of their business model. MS Food City in Debe, Trinidad, is shaping the digital grocery ecosystem and has established its role as the local leader in digital grocery transformation.
Ravil Sookhoo, owner of MS Food City and MS Superstore supermarkets, currently provides his customers with an extensive range of grocery and household items. Many items found on his shelves are manufactured in the back-end warehouse and custom branded with his registered trademark Essentials. Kitchen items ranging from plastic bowls, cups and trays to name a few, line store shelves in his signature teal color; all of sound quality and offered at affordable prices. He believes that to survive this uncertain period and succeed in the long term, grocers must proactively design strategies combining the grocery shopping experience with the benefits of the digital world. This required a transformation in the MS business model to include an expansive, technologically advanced digital grocery ecosystem that will deliver customer satisfaction, profit, and growth for his business.
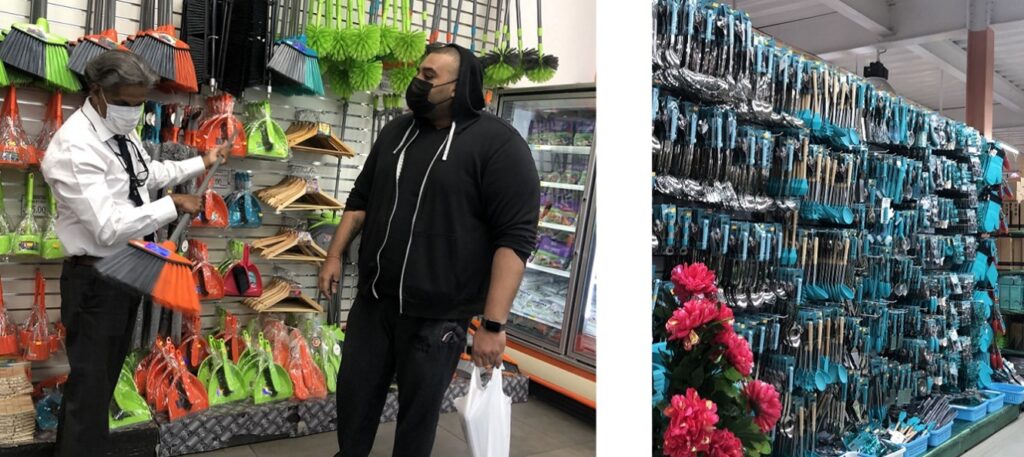

Ravil and his team developed his own custom, digital ecosystem model that offers the consumer a high-quality website and app for merchandising of his products in the digital store, online order fulfillment, dependable logistics, delivery or pickup options and reliable multichannel convenience. He has reallocated space and resources in his warehouses and now has a state-of-the-art system for storage and order fulfillment which contains a Communication center set up with fiber connections and signals specific to warehouse controls. Advanced IT and supply-chain management systems have been implemented for a smooth, order picking, and packing process by using robotics and software. Sophisticated GPS systems allow for easy dispatch to the customer if delivery is required. Ravil’s digital ecosystem model is shaping the future of retail.
Ravil’s business strategy is in line with IDB’s Vision 2025 objectives of digital transformation and reactivation of the productive sector through the encouragement of higher investment in better quality infrastructure and digital connectivity; digitalization and faster adoption of new technologies; entrepreneurship and innovation. His approach also satisfies the Country Strategy objectives by improving the business environment to enable digital transformation and by enhancing the delivery of services. There is an opportunity right here, for collaboration with the IDB Group with opportunities to provide advisory services on digital transformation and financing of operations.

The opportunity in digital transformation and the IDB
As we recover from the impacts of Covid-19, Trinidad and Tobago has a chance to make a significant step change in our digital transformation journey. The actions retailers like Ravil Sookhoo take now in the grocery ecosystem will certainly define what the industry becomes going forward in the post-pandemic era and also help satisfy IDB’s very own Vision 2025 and Country Strategy digital transformation objectives. Ravil may have the means and the know-how to successful transform his business model, but as we will explore in the next case, this is not the case for most vendors trying to transform and the role of the IDB is critical for digital change. Facilitating access and creating the capacity to embrace digital technologies and foster innovation is the first step in IDB’s role of shaping the future of retail in Trinidad and Tobago and helping improve the lives of its people.


